Parisi coaches have a chance to be more than motivators, they are also educators. But how do we teach our older athletes how the body works. The trick is to keep it simple. The more they understand about function and muscle recruitment the better off they will be when they become independent exercisers.
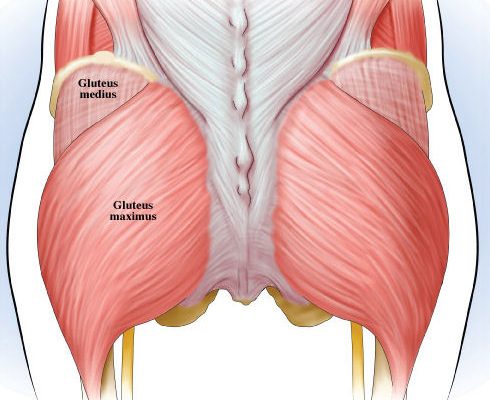
The glute medius:
1. stabilizes the hips
2. helps to externally rotate the thigh
3. assists with forward and upward propulsion
4. assists with lateral movement
The gluteus medius originates on the high outside of the hip. The insertion of the G-medius converges on a tendon that attaches to the lateral surface of the hip joint.
Although the glute-medius assists in many movements, it’s primary responsibility is to prevent the pelvis from rotating downward. Like any over-compensation, injuries are likely to occur when the pelvis is ‘sagging’ when you walk or play a sport.